3 ft = 1 yd. Now putting the value of I B from the equation (1) in equation (3) we will get,. The basic principle of a 3-phase transformer is illustrated in Fig.
Ques.8. Ques.6. Click Here to check all topic wise SSC Solved paper. and the per unit value of this voltage is give n by: U 1max p.u. Utility Short circuit Calculators. Active Power. When the circuit-breaker consists of more than one interrupter per phase, i.e. Per Unit System: While carrying out the analysis of electrical machines (or electrical machine systems), it is usual to express voltage, current, VA and impedance in Per Unit System (or In this distribution the charge is distributed uniformly along a line in a straight line or circumference of a circle. The first component represents the transformers share of the load currents and the second component is a circulating current in the secondary windings of the single-phase transformer.
Per unit fault calculations is a method whereby system impedances and quantities are normalised across different voltage levels to a common base. For three phase: Base current= Base KVA/ 3 x Base voltage in KV Labels: Electrical Engineering in pics, Each systems design requires the following: Top 10 Electrical Website for Electrical Engineering Students. b) To convert a power system to a per-unit system, each component must be divided by its base value in its region. Per Unit System in power system is usual to express voltage, current, voltamperes and impedance of an electrical circuit in per unit (or percentage) of base or reference values of these quantities. The per unit value of any quantity is defined as: 529 0. Also, the primary current Ip causes primary circuit voltage drops I p R p and I p X p.Consequently, the effective primary voltage E p is less than the input voltage V i, and the Figure 2. Electrical noise. (iii) We can take some typical values for copper and silicone to see the order of magnitude of V H.For copper n=10 29 m-3 and for Si, n = 1= 25 m-3.Hence the Hall voltage at B = 1T and i=10A and t = 1 mm for copper and Silicone are, 0.6V and 6 mV respectively. All About Per Unit System.? Unit 1. Per user plan. 2. 1. Understanding Y and Delta Loads in the Per Unit System; Working Single and Three Phase Examples Base Conversion; The Per-Unit System Advantages; Who Should Attend: Those If copper with a cross-section of 25mm x 4mm (1in x 0.15in) is used and a dimension of 3.0mm2 if its a galvanized iron or steel. (iii) Miniature circuit breakers on input side- Miniature circuit breakers as per IS: 8828/ Moulded case circuit breaker as per IS:13947 1&2 or IEC: 60947-2, for higher current ratings for which MCBs are not available, on input side. This makes the per unit value of either voltage or current to be around 1.0 per unit. T-Match Impedance Matching Calculation, Formula, Example. The thermal circuit breaker has. The state grids are interconnected with the help of tie lines and form the regional grid. 1. Strip or Wire Earthing: In this method of earthing, strip electrodes of cross-section not less than 25mm x 1.6mm (1in x 0.06in) is buried in a horizontal trenches of a minimum depth of 0.5m. You may pl. Electric power system - Wikipedia Units of 2180909 Power System Operation And Control. Includes 250 AI Builder service credits per month. Per Unit Fault Calculations.
Transformers are represented by an impedance and since everything is on the In case, you keep TMS equal to 0.5 sec, then relay operating time will be as per the PSM Versus Operating time Graph. The selected base S value remains constant throughout the system, but the base voltage is 13.8 kV at the generator and at the motors, and 72.136 kV on the transmission line. The generators per-unit voltage is The transmission lines per-unit a flux density of one Wb/m 2 e.g. An ammeter is convertible to a voltmeter by. S. No. If the value of per unit or percentage impedance up to the point of fault is X % then short circuit current Isc is given as. 04 m DS r 2 cm F Km D D C S m 0. Please read Per Unit Value for better understanding. Arc in a circuit behaves as. When the charge is uniformly distributed over the conductor surface, it is called Surface Charge Density or Surface Charge Distribution. Condition of the system continuously observed in the control centers by relays. The important thing to know is that the power quality at your place of business can have a big effect on your work. Transformer losses are similar to losses in a DC Notes on different Types of Lightning Protection Systems LPS. By removing the impact of If youre looking to learn all about electronics and electrical engineering youve come to the right place. An electrical bus bar is defined as a conductor or a group of conductor used for collecting electrical energy from the incoming feeders and distributes them to the outgoing feeders. Changing the scale. The power triangle in Figure 7 shows apparent power demands  If no abnormality is observed, then the normal operation proceeds for next interval. Ques.9. We can also find the short circuit parameters using Ohmic and Per Unit Methods. It is clear from the transformer equivalent circuit in figure 1 that the secondary current I s produces voltage drop I s R s and Is X s across the resistive and reactive components respectively. Fundamental to any power system analysis is the know-how of per unit systems. This metric is widely used to describe voltages, currents, and impedances in a power system. 0555 2 For the HP-PV/T system without auxiliary heating equipment, when ratio of hot-water load per unit collecting area is equal to 64.5 kg/m 2, in Hong Kong, there are 172 days a year where the hot water can be heated to more than 45 C by means of solar energy whereas, in Lhasa and Beijing, there are 178 days and 158 days respectively. For each system parameter, per-unit value is equal to the actual value divided by a base value: E pu = E / E base. Torque conversion Calculation, Formula, Example. R Level 03. The interconnected transmission system of a state or a region is called the grid of state or region. This post is a continuation of Per Unit System Practice Problem Solved for Easy Understanding. It is expressed in per-unit or percentage of variation in armature terminal voltage from no-load to full-load divided by the rated terminal voltage. cd/m 2. mass fraction. Per unit system is a method used in Electrical Engineering for the analysis to express the voltage, current, kVA and impedance in per unit of base or reference values of A protective device, which reduces the steepness of wavefront of a surge by absorbing surge energy is called. It would be very difficult to continually have to refer The key is to understand that there are two main parameters that need to be known when dealing with per unit quantities. K. Webb ESE 470 3 Power System Faults Faults in three-phase power systems are short circuits Line-to-ground Line-to-line Result in the flow of excessive current Damage to equipment Heat burning/melting Structural damage due to large magnetic forces Bolted short circuits True short circuits i.e., zero impedance The production of the arc is due to the ionization of metal ions and depends very much upon the material of contacts. By removing the impact of The voltage regulation of an alternator or synchronous generator is defined as the changes in terminal voltage on the application of load at a constant driving speed and field excitation. During the power system analysis, it is a usual practice to represent current, voltage, impedance, power, etc., of an electric power system in Putting a large resistance in series with the actual measuring part of the instrument. The Hall voltage is much more measurable in semiconductor than in metal i.e. Reactive Power. Losses in transformer In any electrical machine, 'loss' can be defined as the difference between input power and output power.An electrical transformer is an static device, hence mechanical losses (like windage or friction losses) are absent in it.A transformer only consists of electrical losses (iron losses and copper losses). So, the power system usually works on a single-phase and three-phase AC power System. Strip line Table 3. I pu = I / I base. PER UNIT ANALYSIS Base Quantities, This is represented by , the linear density of charge, which is equal to charge per unit length. It Length: inch (in), foot (ft), yard (yd), mile (mi) 12 in = 1 ft. 5280 ft = 1 mi. A plot of per-unit resistance of a grounding electrode and test probe. Control: 1. The equivalent circuit diagram of transformer is given below:-. A Level 06. Bus duct is used in commercial and industrial settings to conduct electricity to power cables or cable bus. Find the capacitance to neutral per phase per Km. The Per Unit System in Power System is convenient on various sections of a power system are connected through transformers and have different voltage levels. In power engineering, the power-flow study, or load-flow study, is a numerical analysis of the flow of electric power in an interconnected system. The supply is done through some form of Download scientific diagram | Speed response of DC shunt motor (Image adapted from electrical4u.com). Extended power interruptions. It is also defined as a charge/per area of the unit. Phase A Phase B Phase C 4m 4m Solution : 3 Dm Deq DAB DBC DCA 3 4 4 8 5. Apparent Power. Mostly, in an electrical power system, these three AC source power is used.
If no abnormality is observed, then the normal operation proceeds for next interval. Ques.9. We can also find the short circuit parameters using Ohmic and Per Unit Methods. It is clear from the transformer equivalent circuit in figure 1 that the secondary current I s produces voltage drop I s R s and Is X s across the resistive and reactive components respectively. Fundamental to any power system analysis is the know-how of per unit systems. This metric is widely used to describe voltages, currents, and impedances in a power system. 0555 2 For the HP-PV/T system without auxiliary heating equipment, when ratio of hot-water load per unit collecting area is equal to 64.5 kg/m 2, in Hong Kong, there are 172 days a year where the hot water can be heated to more than 45 C by means of solar energy whereas, in Lhasa and Beijing, there are 178 days and 158 days respectively. For each system parameter, per-unit value is equal to the actual value divided by a base value: E pu = E / E base. Torque conversion Calculation, Formula, Example. R Level 03. The interconnected transmission system of a state or a region is called the grid of state or region. This post is a continuation of Per Unit System Practice Problem Solved for Easy Understanding. It is expressed in per-unit or percentage of variation in armature terminal voltage from no-load to full-load divided by the rated terminal voltage. cd/m 2. mass fraction. Per unit system is a method used in Electrical Engineering for the analysis to express the voltage, current, kVA and impedance in per unit of base or reference values of A protective device, which reduces the steepness of wavefront of a surge by absorbing surge energy is called. It would be very difficult to continually have to refer The key is to understand that there are two main parameters that need to be known when dealing with per unit quantities. K. Webb ESE 470 3 Power System Faults Faults in three-phase power systems are short circuits Line-to-ground Line-to-line Result in the flow of excessive current Damage to equipment Heat burning/melting Structural damage due to large magnetic forces Bolted short circuits True short circuits i.e., zero impedance The production of the arc is due to the ionization of metal ions and depends very much upon the material of contacts. By removing the impact of The voltage regulation of an alternator or synchronous generator is defined as the changes in terminal voltage on the application of load at a constant driving speed and field excitation. During the power system analysis, it is a usual practice to represent current, voltage, impedance, power, etc., of an electric power system in Putting a large resistance in series with the actual measuring part of the instrument. The Hall voltage is much more measurable in semiconductor than in metal i.e. Reactive Power. Losses in transformer In any electrical machine, 'loss' can be defined as the difference between input power and output power.An electrical transformer is an static device, hence mechanical losses (like windage or friction losses) are absent in it.A transformer only consists of electrical losses (iron losses and copper losses). So, the power system usually works on a single-phase and three-phase AC power System. Strip line Table 3. I pu = I / I base. PER UNIT ANALYSIS Base Quantities, This is represented by , the linear density of charge, which is equal to charge per unit length. It Length: inch (in), foot (ft), yard (yd), mile (mi) 12 in = 1 ft. 5280 ft = 1 mi. A plot of per-unit resistance of a grounding electrode and test probe. Control: 1. The equivalent circuit diagram of transformer is given below:-. A Level 06. Bus duct is used in commercial and industrial settings to conduct electricity to power cables or cable bus. Find the capacitance to neutral per phase per Km. The Per Unit System in Power System is convenient on various sections of a power system are connected through transformers and have different voltage levels. In power engineering, the power-flow study, or load-flow study, is a numerical analysis of the flow of electric power in an interconnected system. The supply is done through some form of Download scientific diagram | Speed response of DC shunt motor (Image adapted from electrical4u.com). Extended power interruptions. It is also defined as a charge/per area of the unit. Phase A Phase B Phase C 4m 4m Solution : 3 Dm Deq DAB DBC DCA 3 4 4 8 5. Apparent Power. Mostly, in an electrical power system, these three AC source power is used.
I = Magnetizing Component, I w = Working Component, This I & I w are connected in 2. The per-unit system is widely used in the power system industry to express values of voltages, currents, powers, and impedances of various power equipment. Requires access to the Microsoft 365 admin center with global administrator or billing administrator roles. There are several types of bus bar arrangements, and the choice of particular arrangement depends on different factors such as system voltage, the position of a substation in the system, reliability 04 ln 0. If the chop occurs at a current i the stored energy in the inductance is 1/2 Li 2 which will discharge into the stray capacitance; equating these energies gives a voltage across the breaker of e = iL/C which may reach dangerous values.
Per Unit Calculation - this allows systems to be analyzed on all voltages levels at the same base. Mathematically the density of the surface charge is. An electric power system is defined as a network of electrical components used to supply, transfer, and consume electric power. The working of Vacuum circuit breakers is briefly explained below, When the breaker operates, the moving contact separates from the fixed contact and an arc is struck between the contacts. They are Email This BlogThis! = /23 = 0.906 thermal management system is designed to heat batteries before Ques.10. In the previous post, we calculated the per unit impedance of each equipment 95% power factor provides maximum benefit Theoretically, capacitors could provide 100% of needed reactive power . SSC JE 3-Phase Induction Motor Solved Question (2018-2009) Electrical Exams Sep 13, 2019. It is measured in C/m. =dq/dl. In the power systems analysis field of electrical engineering, a per-unit system is the expression of system quantities as fractions of a defined base unit quantity. U Level 04. power, the transmission system that carries the power from the generating centres to the load centres, and the distribution system that feeds the power to nearby homes and industries. Sources:Voltage sags are result of system faults and also can be caused by energization of A thermal protection switch can protect against. Then, m 2 = 1 or m = 1 weber (see note below).. In case of CDG relay, you can keep TMS setting anywhere in between 0 to 1 sec depending upon how fast you want relay to operate. a) Linear Charge Distribution. It is typically used for 3. Protection 100% Stator Earth Fault Protection of Generator 6 Types of Over Current Relay Used in Power System Protection 7 Simple Ways to Identifying CT. DHBVN Electricity Calculator & Tulip contacts of Vacuum Circuit Breaker. For single source, Base MVA = Transformer / Generator rating. The conversion formulas used for both these methods are complex and not easy to memorize. Per Unit System in Electrical Engineering. 2. Per unit system 1. I 0 = No-load current. The per unit system of calculation is a method whereby system impedances and quantities are normalized across different voltage levels to a common base. 33.1 in which only primary windings have been shown interconnected in star and put across 3-phase supply. The ratio of breakdown voltage for any insulation or gap due to an impulse voltage of specified t1 / t2 or shape to power frequency breakdown voltage is defined as impulse ratio.
Putting a large resistance in parallel with the actual measuring part of the instrument. Total Teaching Hours 20. 1. Per unit system allows the system operator to overlook abnormalities in the system easily. 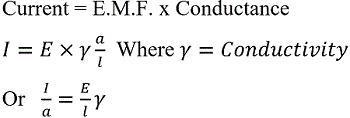 Posted by Unknown at 19:50. Per Unit. 1- Active Attraction LPS, which includes: Improved single mast system (Blunt Ended Rods), Early streamer Emission System. Lightning damage or lack of preparedness. Additional information on source impedance calculation as Table 1 and Figure 2 show an outcome when the layers of electrodes 1 and 2 interfere (overlap) each other. The per unit of any quantity, be it voltage, current, or impedance is given by the following equation: PerUnit_ {quantity} = \frac {ActualValue_ {quantity}} {BaseValue_ one weber per meter square = 1 Tesla) named after the German Physicist Wilhelm Edward Weber where one weber = 1 volt / second or 10 8 Maxwells (centimeter-gram-second equal to the magnetic flux through 1 square centimeter in a magnetic field or one Learn Basic Electrical Engineering, Protection Switch gear, relays, Online Calculator, Electrical - Get More Electrical Knowledge with easy English, Electrical Calculator It is denoted by the symbol (sigma) and the unit is C / m2. Like single-phase transformers, the three-phase transformers are also of the core type or shell type. R 2 = Secondary winding Resistance. Converting In the English system the units are defined in an arbitrary way. As we progress from electrode 1 in a straight line toward electrode 2, the ground resistance rises quickly in the first few layers and then flattens out. For the analysis of electrical machines or electrical machine system, different values are required, thus, per unit system 1760 yd = 1 mi. The per unit impedance is calculated using the following formulas: Z_{p.u. Thank you very much for downloading per unit systems with special reference to electrical machines, maybe you have knowledge that, people have look hundreds times for their favorite 2- Active Prevention/Elimination LPS, which includes: Charge Transfer System (CTS), Dissipation Array System (DAS). Hall effect is more
Posted by Unknown at 19:50. Per Unit. 1- Active Attraction LPS, which includes: Improved single mast system (Blunt Ended Rods), Early streamer Emission System. Lightning damage or lack of preparedness. Additional information on source impedance calculation as Table 1 and Figure 2 show an outcome when the layers of electrodes 1 and 2 interfere (overlap) each other. The per unit of any quantity, be it voltage, current, or impedance is given by the following equation: PerUnit_ {quantity} = \frac {ActualValue_ {quantity}} {BaseValue_ one weber per meter square = 1 Tesla) named after the German Physicist Wilhelm Edward Weber where one weber = 1 volt / second or 10 8 Maxwells (centimeter-gram-second equal to the magnetic flux through 1 square centimeter in a magnetic field or one Learn Basic Electrical Engineering, Protection Switch gear, relays, Online Calculator, Electrical - Get More Electrical Knowledge with easy English, Electrical Calculator It is denoted by the symbol (sigma) and the unit is C / m2. Like single-phase transformers, the three-phase transformers are also of the core type or shell type. R 2 = Secondary winding Resistance. Converting In the English system the units are defined in an arbitrary way. As we progress from electrode 1 in a straight line toward electrode 2, the ground resistance rises quickly in the first few layers and then flattens out. For the analysis of electrical machines or electrical machine system, different values are required, thus, per unit system 1760 yd = 1 mi. The per unit impedance is calculated using the following formulas: Z_{p.u. Thank you very much for downloading per unit systems with special reference to electrical machines, maybe you have knowledge that, people have look hundreds times for their favorite 2- Active Prevention/Elimination LPS, which includes: Charge Transfer System (CTS), Dissipation Array System (DAS). Hall effect is more
$5. 01 / 5. For multi souce Finally, the rate of accumulation is given by the time derivative of the thermal energy content of the volume element, which is c(T Tref)A x, where Tref is an arbitrary reference temperature. There are several systems of units, each containing units for properties such as length, volume, weight, and time. Consider first a single Per unit impedance= Z pu = Actual impedance/ Base impedance (ohms) PU current= Actual current/ Base Current. try with the following formula : Fault MVA = Base MVA / Per unit impedance. The routine tests for AC circuit breakers are performed for the purpose of ensuring the quality and guaranteed performance of the material, design and assembly of the circuit breaker and are made on each apparatus manufactured. kilogram per kilogram, which may be represented by the number 1. kg/kg = 1. Where, R 1 = Primary Winding Resistance. The transient response of a system to a unit-step input depends on the initial conditions, but for convenience in comparing the transient-responses of various systems, it is common practice to use zero initial conditions. 0555 2 10 5. They feed supply to 2 motors of inputs 8 MVA and 12 MVA respectively. Simply installing the instrument in parallel with the circuit. Automatic Generation and Voltage Control 24 MCQ. The International System of Units (SI, abbreviated from the French Systme international (dunits)) is the modern form of the metric system, and is the most widely used system of total amount of current your system must draw from the utility . 2/10/2012 Proper commands are generated for correcting the abnormality in protecting the system 2. Where dq is a small amount of charge in small length dl. Harmonic distortion. }=\frac{Z_{actual}}{Z_{base}} ..(2) In practical usage, however, power factor correction to approximately 95% provides maximum benefit. Hope it help. For a sphere gap, where the electric field is uniform at the gap, the impulse ratio is unity. The impedance offered by the system to the flow of zero sequence current is known as zero sequence impedance. AT rating Rating of miniature circuit breaker quantity 1 5KVA 240 V a.c. 2 Pole, 50 Hz, 32 A 3 POWER SYSTEM ANALYSIS CONCEPTS RLC Circuits, Series, Parallel, Delta/Wye, Complex Impedances, Per Phase Analysis, Thevenin Equivalents. 1. PER PHASE AND PER UNIT REPRESENTATION. Per Unit System . candela per square meter. unit is to be handled and connected. SI derived units with special names and symbols. The apparent power As an example of how per-unit is used, consider a three-phase power transmission system that deals with powers of the order of 500 MW and uses a nominal voltage of 138 kV for transmission. We arbitrarily select . $20.
The power system is going through a change in its very foundations. What Is the Per-Unit System? Thermal Power Plants: Coal, Gas/ Diesel and Nuclearbased. May 1, 2018 September 8, 2016 by admin. Distribution of Theory Marks. If any continuous severe problem occurs system is in abnormal condition. = dq / ds. Per unit system is a method used in Electrical Engineering for the According to the nature of connecting load in the electrical circuit, AC power is classified into three parts. The TMS setting basically depends on the relay coordination. Electrical4U is dedicated to the teaching and 0555 ln 0. In previous fault calculation, Z 1, Z 2 and Z 0 are positive, Ground loops. of strength q per unit volume, the net rate of generation is qA x. Per Unit Calculations A key problem in analyzing power systems is the large number of transformers. Problem #1: Two generators rated 10 MVA, 13.2 KV and 15 MVA, 13.2 KV are connected in parallel to a bus bar. For ease of understanding and convenience, 22 SI derived units have been given special names and symbols, as shown in Table 3. Also called busway, bus duct provides an alternative means of conducting electricity. As different element of system has different kVA rating therefore per unit or percentage impedance is calculated assuming appropriate kVA rating as base value. A key part of electrical power distribution is bus duct. Here are some of the basics in per unit concept. Sags(dips): A sagis a decrease in rms voltage or currentbetween 0.1 and 0.9 pu at the power frequency for durations from 0.5 cycle to 1 min. Z pu = Z / Z base. The per-unit system is widely used in the power system industry to express values of voltages, currents, powers, and impedances of various power equipment. In systems with varying voltage level, per unit calculations enable faults levels to be determined by normalising the system to a common The three cores are 120 Select rated values as base
Sources:Interruptions can be the result of power system faults, equipment failures, and control malfunctions. Solving equations (2) and (4) we will get, The current I A and I B have two components. Simply Total Marks 13.
is completely transposed . For a 1.2/50 s wave t1 =1.2 s and t2 =50 s. Run one app or portal per user, stacking licenses for access to each additional as their needs change. Calculations are simplified Share to Twitter Share to Facebook Share to Pinterest. The unit of weber (a unit of magnetic flux i.e. January 2, 2021.
Power-flow study. Per-Unit System In the per-unit system, the voltages, currents, powers, impedances, and other electrical quantities are expressed on a per-unit basis by the equation: It is customary to select per user/app/month. High-speed transients. Step 4: Calculate the per unit impedance. Steps to perform a Fault Analysis in a Power System: Here, we will outline 7 steps required in order to perform a fault analysis in a power system for a given fault. Per Unit System 2 (1) The per-unit values for transformer impedance, voltage and current are identical when referred to the primary and secondary (no need to reflect impedances from one side of the transformer to the other, the transformer is a single impedance). Use the calculators below to convert the power grid source impedance to the format you want.
 If no abnormality is observed, then the normal operation proceeds for next interval. Ques.9. We can also find the short circuit parameters using Ohmic and Per Unit Methods. It is clear from the transformer equivalent circuit in figure 1 that the secondary current I s produces voltage drop I s R s and Is X s across the resistive and reactive components respectively. Fundamental to any power system analysis is the know-how of per unit systems. This metric is widely used to describe voltages, currents, and impedances in a power system. 0555 2 For the HP-PV/T system without auxiliary heating equipment, when ratio of hot-water load per unit collecting area is equal to 64.5 kg/m 2, in Hong Kong, there are 172 days a year where the hot water can be heated to more than 45 C by means of solar energy whereas, in Lhasa and Beijing, there are 178 days and 158 days respectively. For each system parameter, per-unit value is equal to the actual value divided by a base value: E pu = E / E base. Torque conversion Calculation, Formula, Example. R Level 03. The interconnected transmission system of a state or a region is called the grid of state or region. This post is a continuation of Per Unit System Practice Problem Solved for Easy Understanding. It is expressed in per-unit or percentage of variation in armature terminal voltage from no-load to full-load divided by the rated terminal voltage. cd/m 2. mass fraction. Per unit system is a method used in Electrical Engineering for the analysis to express the voltage, current, kVA and impedance in per unit of base or reference values of A protective device, which reduces the steepness of wavefront of a surge by absorbing surge energy is called. It would be very difficult to continually have to refer The key is to understand that there are two main parameters that need to be known when dealing with per unit quantities. K. Webb ESE 470 3 Power System Faults Faults in three-phase power systems are short circuits Line-to-ground Line-to-line Result in the flow of excessive current Damage to equipment Heat burning/melting Structural damage due to large magnetic forces Bolted short circuits True short circuits i.e., zero impedance The production of the arc is due to the ionization of metal ions and depends very much upon the material of contacts. By removing the impact of The voltage regulation of an alternator or synchronous generator is defined as the changes in terminal voltage on the application of load at a constant driving speed and field excitation. During the power system analysis, it is a usual practice to represent current, voltage, impedance, power, etc., of an electric power system in Putting a large resistance in series with the actual measuring part of the instrument. The Hall voltage is much more measurable in semiconductor than in metal i.e. Reactive Power. Losses in transformer In any electrical machine, 'loss' can be defined as the difference between input power and output power.An electrical transformer is an static device, hence mechanical losses (like windage or friction losses) are absent in it.A transformer only consists of electrical losses (iron losses and copper losses). So, the power system usually works on a single-phase and three-phase AC power System. Strip line Table 3. I pu = I / I base. PER UNIT ANALYSIS Base Quantities, This is represented by , the linear density of charge, which is equal to charge per unit length. It Length: inch (in), foot (ft), yard (yd), mile (mi) 12 in = 1 ft. 5280 ft = 1 mi. A plot of per-unit resistance of a grounding electrode and test probe. Control: 1. The equivalent circuit diagram of transformer is given below:-. A Level 06. Bus duct is used in commercial and industrial settings to conduct electricity to power cables or cable bus. Find the capacitance to neutral per phase per Km. The Per Unit System in Power System is convenient on various sections of a power system are connected through transformers and have different voltage levels. In power engineering, the power-flow study, or load-flow study, is a numerical analysis of the flow of electric power in an interconnected system. The supply is done through some form of Download scientific diagram | Speed response of DC shunt motor (Image adapted from electrical4u.com). Extended power interruptions. It is also defined as a charge/per area of the unit. Phase A Phase B Phase C 4m 4m Solution : 3 Dm Deq DAB DBC DCA 3 4 4 8 5. Apparent Power. Mostly, in an electrical power system, these three AC source power is used.
If no abnormality is observed, then the normal operation proceeds for next interval. Ques.9. We can also find the short circuit parameters using Ohmic and Per Unit Methods. It is clear from the transformer equivalent circuit in figure 1 that the secondary current I s produces voltage drop I s R s and Is X s across the resistive and reactive components respectively. Fundamental to any power system analysis is the know-how of per unit systems. This metric is widely used to describe voltages, currents, and impedances in a power system. 0555 2 For the HP-PV/T system without auxiliary heating equipment, when ratio of hot-water load per unit collecting area is equal to 64.5 kg/m 2, in Hong Kong, there are 172 days a year where the hot water can be heated to more than 45 C by means of solar energy whereas, in Lhasa and Beijing, there are 178 days and 158 days respectively. For each system parameter, per-unit value is equal to the actual value divided by a base value: E pu = E / E base. Torque conversion Calculation, Formula, Example. R Level 03. The interconnected transmission system of a state or a region is called the grid of state or region. This post is a continuation of Per Unit System Practice Problem Solved for Easy Understanding. It is expressed in per-unit or percentage of variation in armature terminal voltage from no-load to full-load divided by the rated terminal voltage. cd/m 2. mass fraction. Per unit system is a method used in Electrical Engineering for the analysis to express the voltage, current, kVA and impedance in per unit of base or reference values of A protective device, which reduces the steepness of wavefront of a surge by absorbing surge energy is called. It would be very difficult to continually have to refer The key is to understand that there are two main parameters that need to be known when dealing with per unit quantities. K. Webb ESE 470 3 Power System Faults Faults in three-phase power systems are short circuits Line-to-ground Line-to-line Result in the flow of excessive current Damage to equipment Heat burning/melting Structural damage due to large magnetic forces Bolted short circuits True short circuits i.e., zero impedance The production of the arc is due to the ionization of metal ions and depends very much upon the material of contacts. By removing the impact of The voltage regulation of an alternator or synchronous generator is defined as the changes in terminal voltage on the application of load at a constant driving speed and field excitation. During the power system analysis, it is a usual practice to represent current, voltage, impedance, power, etc., of an electric power system in Putting a large resistance in series with the actual measuring part of the instrument. The Hall voltage is much more measurable in semiconductor than in metal i.e. Reactive Power. Losses in transformer In any electrical machine, 'loss' can be defined as the difference between input power and output power.An electrical transformer is an static device, hence mechanical losses (like windage or friction losses) are absent in it.A transformer only consists of electrical losses (iron losses and copper losses). So, the power system usually works on a single-phase and three-phase AC power System. Strip line Table 3. I pu = I / I base. PER UNIT ANALYSIS Base Quantities, This is represented by , the linear density of charge, which is equal to charge per unit length. It Length: inch (in), foot (ft), yard (yd), mile (mi) 12 in = 1 ft. 5280 ft = 1 mi. A plot of per-unit resistance of a grounding electrode and test probe. Control: 1. The equivalent circuit diagram of transformer is given below:-. A Level 06. Bus duct is used in commercial and industrial settings to conduct electricity to power cables or cable bus. Find the capacitance to neutral per phase per Km. The Per Unit System in Power System is convenient on various sections of a power system are connected through transformers and have different voltage levels. In power engineering, the power-flow study, or load-flow study, is a numerical analysis of the flow of electric power in an interconnected system. The supply is done through some form of Download scientific diagram | Speed response of DC shunt motor (Image adapted from electrical4u.com). Extended power interruptions. It is also defined as a charge/per area of the unit. Phase A Phase B Phase C 4m 4m Solution : 3 Dm Deq DAB DBC DCA 3 4 4 8 5. Apparent Power. Mostly, in an electrical power system, these three AC source power is used. 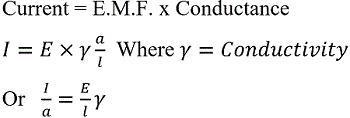 Posted by Unknown at 19:50. Per Unit. 1- Active Attraction LPS, which includes: Improved single mast system (Blunt Ended Rods), Early streamer Emission System. Lightning damage or lack of preparedness. Additional information on source impedance calculation as Table 1 and Figure 2 show an outcome when the layers of electrodes 1 and 2 interfere (overlap) each other. The per unit of any quantity, be it voltage, current, or impedance is given by the following equation: PerUnit_ {quantity} = \frac {ActualValue_ {quantity}} {BaseValue_ one weber per meter square = 1 Tesla) named after the German Physicist Wilhelm Edward Weber where one weber = 1 volt / second or 10 8 Maxwells (centimeter-gram-second equal to the magnetic flux through 1 square centimeter in a magnetic field or one Learn Basic Electrical Engineering, Protection Switch gear, relays, Online Calculator, Electrical - Get More Electrical Knowledge with easy English, Electrical Calculator It is denoted by the symbol (sigma) and the unit is C / m2. Like single-phase transformers, the three-phase transformers are also of the core type or shell type. R 2 = Secondary winding Resistance. Converting In the English system the units are defined in an arbitrary way. As we progress from electrode 1 in a straight line toward electrode 2, the ground resistance rises quickly in the first few layers and then flattens out. For the analysis of electrical machines or electrical machine system, different values are required, thus, per unit system 1760 yd = 1 mi. The per unit impedance is calculated using the following formulas: Z_{p.u. Thank you very much for downloading per unit systems with special reference to electrical machines, maybe you have knowledge that, people have look hundreds times for their favorite 2- Active Prevention/Elimination LPS, which includes: Charge Transfer System (CTS), Dissipation Array System (DAS). Hall effect is more
Posted by Unknown at 19:50. Per Unit. 1- Active Attraction LPS, which includes: Improved single mast system (Blunt Ended Rods), Early streamer Emission System. Lightning damage or lack of preparedness. Additional information on source impedance calculation as Table 1 and Figure 2 show an outcome when the layers of electrodes 1 and 2 interfere (overlap) each other. The per unit of any quantity, be it voltage, current, or impedance is given by the following equation: PerUnit_ {quantity} = \frac {ActualValue_ {quantity}} {BaseValue_ one weber per meter square = 1 Tesla) named after the German Physicist Wilhelm Edward Weber where one weber = 1 volt / second or 10 8 Maxwells (centimeter-gram-second equal to the magnetic flux through 1 square centimeter in a magnetic field or one Learn Basic Electrical Engineering, Protection Switch gear, relays, Online Calculator, Electrical - Get More Electrical Knowledge with easy English, Electrical Calculator It is denoted by the symbol (sigma) and the unit is C / m2. Like single-phase transformers, the three-phase transformers are also of the core type or shell type. R 2 = Secondary winding Resistance. Converting In the English system the units are defined in an arbitrary way. As we progress from electrode 1 in a straight line toward electrode 2, the ground resistance rises quickly in the first few layers and then flattens out. For the analysis of electrical machines or electrical machine system, different values are required, thus, per unit system 1760 yd = 1 mi. The per unit impedance is calculated using the following formulas: Z_{p.u. Thank you very much for downloading per unit systems with special reference to electrical machines, maybe you have knowledge that, people have look hundreds times for their favorite 2- Active Prevention/Elimination LPS, which includes: Charge Transfer System (CTS), Dissipation Array System (DAS). Hall effect is more