The basic equation to use is F (Force) = P (Pressure) x A (Surface Area). The strength of the cylinder tube is proportional to its wall. Extend Volume (in) =. And hydraulic axial piston motors and pumps have 0.87. 2. Hydraulic Cylinder Question 4. 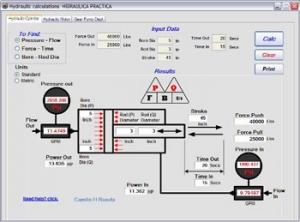 Cylinder Area (sq in) Stroke Length (inches) Stroke Time (seconds) Flow Needed. Calculate the resultant force generated at the piston and transmitted through to the rod, and also determine this forces direction.
Cylinder Area (sq in) Stroke Length (inches) Stroke Time (seconds) Flow Needed. Calculate the resultant force generated at the piston and transmitted through to the rod, and also determine this forces direction.
Hydraulic Rod Cylinder Calculator and flow to get extend, retract, and flows/cycle time values. Push =sin (angle)*PSI*3.1415*b2/4 lbs. CALCULATORS. The approximate admissible buckling load F k is calculated on the basis of the piston rod diameter d s and the buckling length L k.The buckling length L k can be read Total efficiency is volumetric efficiency X mechanical/hydraulic efficiency. Piston Speed. Moreover, the general power loss in a hydraulic energy transmission is around 25% or more at ideal viscosity range 25-35 [cSt]. Welcome to Hydraulics International. Then multiply that number by the maximum plastics pressure we discussed. Standard Cylinders: If the machine cylinder hydraulic pressure is known (and available during injection), minimum bore size is: B = SQRT[(4 x F)/(H x 3.14)] For 2" dia. Call 1-800-728-5168 | Email Us Calculate hydraulic cylinder force. Find hydraulic cylinder formulas for volume, flow rate and fluid motor power. Piston / Bore Diameter mm Rod Diameter mm Stroke mm Pressure bar Oil Flow lpm Bore Side Rod Side Area cm Volume l Force kN Time sec Velocity m/s Outflow lpm Ratio At Womack Machine Supply, we carry Formulas and Calculations for Hydraulic Pumps, Hydraulic Motors, Hydraulic cylinders, Fluid & Piping, Heat, and Data Conversion. pull =sin (angle)*PSI*3.1415* (b2-d2)/4 lbs. Pressure lines over 3000 PSI - 25 ft/sec. mm. Hydraulic cylinders get their power from pressurized hydraulic fluid, which is typically oil. Pneumatic cylinder force calculations formulas includes force calculation, air consumption, Output power. We also provide hydraulic cylinder calculator tools for rod and telescopic cylinders. It is designed to be used by engineers eager to red BFD - Block Flow Diagram - A Block Flow Diagram is a schematic illustration of a major process. GPM = 6 Net Cylinder Area = 28.26 square inches (231 x GPM) (60 x Net Cylinder Area) = (231 x 15) (60 x 28.26) = 2.04 inches per second V - velocity rate of piston rod; Q - flow; Ae - effective area ; Extended speed of cylinder. We also provide hydraulic cylinder calculator tools for rod and telescopic cylinders. Click to Compute the PUSH / PULL *Disclaimer below.
Theoretical Thrust (Cylinders) N = Effective area (sq.cm) x pressure (bar) x 10: Lb = Hydraulics and Pneumatics - Hydraulic and pneumatic systems - fluids, forces, pumps and pistons. Velocity of Oil Flow in a Pipe: Recommended Maximum Oil Velocity in Hydraulic Lines. ; Force Ratio - The force ratio is the load force versus the effort force. Pressure lines to 500 PSI - 10 to 15 ft/sec. 1 - (500/5000) = 1 - 0.1 = 0.90 = 90%.
There is mechanical friction associated with the piston and rod seals. Store. Since volumetric Hydraulic and Pneumatic systems have wide variety of applications in the industry includes automobile, packaging, medical and construction. POWER. Pneumatic systems use compressed air to move object using cylinder, motor or other mechanical parts. Pressure lines to 3000 PSI - 15 to 20 ft/sec. Calculate circle area from diameter; Calculate circle diameter from area; User Guide. Relationship between displacement and torque of a hydraulic motor: T = HP x 63025 RPM HP = T x RPM 63205 RPM = HP x 63025 T Note: Volume Capacity. This tool will calculate the force generated by a piston cylinder for a specified pneumatic/hydraulic pressure and piston-cylinder bore diameter. Cylinder Blind End Area (in square inches) PI X (Cylinder Radius) ^2.Cylinder Output Force (in Pounds) Pressure (in PSI) X Cylinder Area.Fluid Pressure in PSI Required to Lift Load (in PSI) Pounds of Force Needed / Cylinder Area.Cylinder Speed (in inches per second)GPM of Flow Needed for Cylinder Speed. Common Hydraulic Cylinder Formulas. The approximate buckling load of hydraulic cylinders is checked using Euler's method of calculation. Hydraulic Pumps & Motors. Hydraulic Cylinders. 1 BTU/hr = .0167 BTU/min = .00039 hp. in (I.D. For < s applies s = 0,09 r RPM. Hydraulic Cylinder Formulas; Cylinder Formulas For: Word Formula Overall efficiency is simply the product of volumetric and mechanical/hydraulic efficiency.
(Push force = PSI x Area) 3.Determine the bore size of your cylinder. TIP: There are online calculators available, where you simply plug in the values to get the result. Diameter - Typical hydraulic cylinders and acting area There is also fluid friction as fluid enters and exits the cylinder. Click to Compute the PUSH / PULL *Disclaimer below. core and H = 1,500 psi: = 7.3 inches (8" bore cylinder) For other injection pressures and core area, see Chart 1.. Nonstandard Cylinders: Preloading side-action cylinders generate the large output forces of Cylinders normally have a total efficiency of around 0.95. where p = pressure in psi, d = dia of cylinder in inches, t = thickness of cylinder, Fs = stress permissible. 2. Download Don's infamous Hydraulic Calculator Cheat Sheet. 1,30 1,00 0,50 0,00 10-5 10-4 10-3 10-2 10-1 100 0,06 lx / d Re s Figur 1: The disturbance source factor s as function of x dRe. The cylinder force is found by multiplying the full cylinder force times the sine (sin) of the least angle between cylinder and lever axes. F1 = rod force (lb, N)d1 = rod diameter (in, m)d2 = piston diameter (in, m)P1 = pressure in the cylinder on the rod side (lff/in2 (psi), N/m2 (Pa)) Cylinder Force, FF, is horizontal in this figure. (Push force = PSI x Area) Cylinder Blind End Area = 28.26 square inches Rod Diameter = 3" Radius is 1/2 of rod diameter = 1.5" ; Related Documents . The tube thickness of a cylinder barrel is a very important factor in the design of a hydraulic cylinder . An admissible buckling load F k is determined which the cylinder's extending force F 1 must not exceed.. Formula. Pressure lines to 3000 PSI - 15 to 20 ft/sec. part of the cylinder force is effective on the lever. Example: How many GPM are needed to extend a 6" diameter cylinder 8 inches in 10 seconds? Follow these 3 steps to calculate the required maximum power output for the diesel engine. 4. Cylinder diameter =. During our Engineering College studies, in Applied Mechanics subject, we studied that the formula for calculating thickness for a cylinder is (p x d)/ x 2t = Fs. DHAYAYANANDHAN.S. Horsepower (hp) = pressure (psi) x flow (gpm) / 1714 -or- BTU/hr = 1 x psi x gpm. Formula. mounted at an angle. Mobile Cylinder Division Youngstown, OH Formulas HYDRAULIC MOTOR EQUATIONS Note: Hydraulic motors are typically classified as high speed motors (500 - 10,000 rpm) or low speed motors (0 - 1,000) rpm. Quantity =. FLOW. Formula: Cylinder Area x Stroke Length in Inches 231 x 60 Time in seconds for one stroke = GPM. cylinder force ; in kilograms (kg) kg= 10.1 cm x 10.1 cm x 180 bar x 3.14 4 = 14414 kg tons= kg 1000 14414 kg 1000 = 14.41 tons cylinder capacity flow rate ; It's written in Microsoft Excel but should work just fine imported into Google Drive. Pressure lines to 500 PSI - 10 to 15 ft/sec. Hydraulic cylinders get their power from pressurized hydraulic fluid, which is typically oil. The internal diameter of your pipe in inches. pcs. These formulas are helpful for those working with hydraulic cylinders. Home > System Design > Engineering & Design > Hydraulic Formulas. 2. mm. * Bore Diameter (in). * Bore Diameter (in). Also include fluid motor torque/100 psi, fluid motor speed and more. Extend / Retract Time in Seconds. Pump suction lines - 2 to 4 ft/sec. 2.Accurately calculate the cavity surface that is on the surface area of the component. LPM. The approximate admissible buckling load F k is calculated on the basis of the piston rod diameter d s and the buckling length L k.The buckling length L k can be read CALCULATE CYLINDER. Please note a fully qualified hydraulic technician will be required to ensure your system setup is correctly configured and safe. These formulas are helpful for those working with hydraulic cylinders. Now that you have formulated the working area of the systems cylinder you can plug that data into the formula below and calculate the push force of your hydraulic cylinder. In a modern hydraulic cylinder, where volumetric efficiency approaches 100%, overall efficiency equals mechanical/hydraulic efficiency: 0.95 x 1 = 0.95 = 95%. Variety of calculators for hydraulic cylinders and hydraulic pumps. Line Sizing And Fluid Velocity In Hydraulic SystemsLine size selection. Selecting the proper line size for a hydraulic system is critical to get maximum performance and life from your hydraulic components.Fluid Velocity: Velocity = GPM x 0.3208 Pressure Drop: Pressure drop through the conductor must be accounted for in long runs of pipe, hose or tubing. Conclusion. The turbulant ow is completely developed at the distance s after a disturbance source. Pneumatic Cylinders Market report provides the detailed study of manufacturing sites, area served, product type, competitive situation and trends. Also, this market includes Pneumatic Cylinders players market share by revenue, industry facts and figures by country, recent updates, analysis by type and applications. The approximate buckling load of hydraulic cylinders is checked using Euler's method of calculation. PUSH / PULL for a hydraulic cylinder. Enter the Cylinder Bore diameter, PSI (pressure), Rod Diameter and Angle . Cylinder Flow Rate (gpm) = 12 x 60 x cylinder speed (ft/sec) x area (in) / 231 Cylinder Volume Capacity (gals) = cylinder area (in) x cylinder stroke (ins) / 231 Basic Hydraulic Motor Calculations: Motor Torque (in lbs) = pressure (psi) x motor displacement (cu ins/rev) / 6.28 (Can also use horsepower (hp) x 63,025 / speed (rpm) Force in Pounds. Velocity of Oil Flow in a Pipe: Recommended Maximum Oil Velocity in Hydraulic Lines. Piston diameter =. 2. Basic Hydraulic Motor Calculations: Heat Generation Formulas: Converting heat into other units. * Bore Diameter (in) * Stroke (in) An admissible buckling load F k is determined which the cylinder's extending force F 1 must not exceed.. 4. The velocity at which the piston rod of a hydraulic cylinder moves is based on the following equation: V=Q/Ae. Required input is missing! the cylinder in Newtons; A is the cross section area in square millimeters and p is the force in bar. You can rearrange the equation to solve for pressure using P = F/A. 1. Hydraulic Cylinder Velocity Calculator. Extend Volume (in) =. Now that you have formulated the working area of the systems cylinder you can plug that data into the formula below and calculate the push force of your hydraulic cylinder. Push =sin (angle)*PSI*3.1415*b2/4 lbs. Related Topics . Click to Compute the PUSH / PULL *Disclaimer below. Formula. The internal diameter of your pipe in inches. This is the fluid power formula to calculate hydraulic cylinder speed. The result will be the required pressure for designing your cylinder. of Pipe) 4. Formula: Cylinder Area x Stroke Length in Inches 231 x 60 Time in seconds for one stroke = GPM Cylinder Area (sq in) Stroke Length (inches) Stroke Time (seconds) Flow Needed The formulas and calculators provided on this page give theoretical answers that should only be used as a guide. Displacement in Gallons / Minute. To do so follow the formula below: Area = D^2 (diameter) x /4. ; Hydraulic Cylinder Area vs. Push force = PSI (system pressure) x D^2 (diameter) /4. To do so follow the formula below: Area = D^2 (diameter) x /4. pull =sin (angle)*PSI*3.1415* (b2-d2)/4 lbs. Enter the Cylinder Bore diameter, PSI (pressure) and Rod Diameter. The hydraulic cylinder consists of a cylinder barrel, in which a piston connected to a piston rod moves back and forth.rod moves back and forth. PUSH / PULL for a hydraulic cylinder: 1.
CC. The force produced on the rod side (1) of a double acting hydraulic piston - can be expressed as F1 = P1 ( (d22 - d12) / 4) (1) where F1 = rod force (lb, N) d1 = rod diameter (in, mm) d2 = piston diameter (in, mm) P1 = pressure in the cylinder on the rod side (psi, N/mm2) 1 bar = 105 N/m2 = 0.1 Nm/mm2 It is designed to be used by engineers eager to red E = Young's modulus of the material used in this design calculation is 210 (Gpa) for BS 970 070M20 (Low carbon steel). Pressure lines over 3000 PSI - 25 ft/sec. Pump suction lines - 2 to 4 ft/sec. Flow Rate of a cylinder Q = 60 x A x v Q is flow rate of the cylinder in litres per minute; A is the area in square centimeter and v is velocity of the rod in meters per second. of Pipe) 4.
Hydraulic Calculator 2.0 PC is a software tool that performs the hydraulic calculations needed for cylinders, pumps and motors. If a >cylinder is too thick or too thin may pose serious. 97- calculator pumps 96 calculator cylinder 95 -hydraulic formulae hydraulic workshop formulae. General cylinder speed formula: v = speed of the piston in (m/s) or (m/min) or (cm/s) A = Surface area in (m 2) or (mm 2) or (cm 2) qv = Flow in (L/s) or (L/min) Speed out (extend) Speed in (retract) With the calculated speed we can than easily calculate the time it takes to fully extend or retract the cylinder. Only that portion, EF, which is at right angles to the lever axis is effective for turning the lever. The form-based calculators use our proven formulas for three practical applications; rod and telescopic cylinders. A double-acting hydraulic cylinder has 500 PSI of pressure applied to the side without the rod and 750 PSI of pressure applied to the rod-side. STEP 1 --Hydraulic Cylinder.jpg Cylinder Speed (in inches per second): (231 x GPM) (60 x Net Cylinder Area) Example: How fast will a 6" diameter cylinder with a 3" diameter rod extend with 15 gpm input? The hydraulic cylinder consists of a cylinder barrel, in which a piston connected to a piston rod moves back and forth.rod moves back and forth. Extend Area (in) =. In practice answers can and will vary. Hydraulic cylinder push and pull force calculator, hydraulic cylinder speed calculator, hydraulic pump displacement calculator, hydraulic pump flow rate calculator, hydraulic motor speed calculator by (585) 328-0670 [email protected]. Hydraulic Cylinder Calculations --Double Acting Hydraulic Cylinder.jpg Cylinder Rod End Area (in square inches): Blind End Area - Rod Area Example: What is the rod end area of a 6" diameter cylinder which has a 3" diameter rod? Hydraulic Calculator 2.0 PC is a software tool that performs the hydraulic calculations needed for cylinders, pumps and motors. Enter the Cylinder Bore diameter, PSI (pressure) and Rod Diameter. Hydraulic Formulas. PUSH / PULL for a hydraulic cylinder: 1. Displacement in Cubic Inches / Minute. Separate decimals with a decimal point.
in (I.D. Extend Area (in) =. Push force = PSI (system pressure) x D^2 (diameter) /4.
 Cylinder Area (sq in) Stroke Length (inches) Stroke Time (seconds) Flow Needed. Calculate the resultant force generated at the piston and transmitted through to the rod, and also determine this forces direction.
Cylinder Area (sq in) Stroke Length (inches) Stroke Time (seconds) Flow Needed. Calculate the resultant force generated at the piston and transmitted through to the rod, and also determine this forces direction.