 Answer: Torque required.
Answer: Torque required. Calculate the gross torque developed by the armature of the motor.  Answer: Torque required.
Answer: Torque required.
The armature of all DC motors contains some amount of resistance (Ra). The connection diagram of the DC shunt motor is as shown in the figure below. These characteristics are determined by keeping the following two relations in mind. Make sure that the armature resistance and terminal voltage should be maintained constant while varying the armature current. The electrical work required by the motor for causing the current against the back emf is converted into mechanical energy. 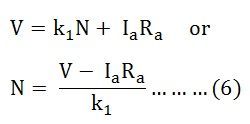 The EMF generated per path for a wave winding & lap-winding; So the generalized equation for generated EMF of DC generator is: Eg = k.
The EMF generated per path for a wave winding & lap-winding; So the generalized equation for generated EMF of DC generator is: Eg = k.  1.7 DESCRIBE the relationship between armature current and torque produced in a DC motor. rearranging the above formula the torque equation of dc motor become. Characteristics of DC motors. A separately excited D.C. motor operating from a single phase half controlled bridge rectifier as a speed of 1400 rpm has an input voltage of 330sin(314t) and aback emf of 80V.
1.7 DESCRIBE the relationship between armature current and torque produced in a DC motor. rearranging the above formula the torque equation of dc motor become. Characteristics of DC motors. A separately excited D.C. motor operating from a single phase half controlled bridge rectifier as a speed of 1400 rpm has an input voltage of 330sin(314t) and aback emf of 80V.
An armature is defined as the component of an electric machine (i.e. A separately excited DC motor has two input power sources, one to the armature circuit and one the field circuit. DC Shunt Motor : In a dc shunt motor field, the winding is connected in parallel with the armature. Here, VI a = Electrical power input to the motor (armature input). Full Load current calculation DC machine (DC Motor & DC generator): DC => Direct Current. E b I a = Electrical equivalent of mechanical power developed in the armature. You know Total Power \$P_T\$ = 11kW and Total Voltage \$V_T\$ = 220V. The connection diagram of the DC shunt motor is as shown in the figure below. The resistance of the armature circuit is 1 and that of the field circuit is 250 . The armature current drawn by a dc motor is proportional to. Shunt and series motors only have one power source, the armature circuit terminals. Armature reaction also occurs in a DC motor just like armature reaction in DC Generator. Power Equation of DC Motor If the eqn. The Torque equation of a DC motor can also be explained considering the figure below.
DC Series Motor : The field winding of these motors is connected in series with the armature and carries the same current. If the armature current of a dc motor is increased keeping the field flux constant, then the developed torque. Example 14-1: An armature-controlled dc motor has the following ratings: T f =0.012 N-m, R a =1.2 ohms, K T =0.06 N-m/A, A direct current (DC) motor is a form of electric machine that converts electrical energy into mechanical energy. DC Motor Equations In a DC drive voltage applied (Va) to the armature circuit is received from a variable DC source. [math]T=Wr [/math], where [math]W [/math] is weight of the load and [math]r [/math] is the wheel radius. Where. The torque equation of a normal motor is given as T e . Voltage applied to the field circuit (Vf) is from a separate source. The speed thus produced be N 1 rpm. Answer: Many motors, while "motoring", are also acting as >>generators<<, generating a so-called "back EMF" which tends to match and cancel out the applied voltage (insofar as that voltage tends to produce a resulting flow of current.) So, we can have an estimate of the armature current by calculating as. Transfer function and state space model are developed for a permanent magnet DC motor. 1.8 DESCRIBE the differences in construction between a shunt-wound and a series-wound DC motor with respect to the relationship between the field and the armature windings. And that energy is induced in the armature of the motor. using the formula E.M.F. For the DC shunt motors, the field current is constant. The armature reaction is the effect of the armature flux on the main flux. You have the field resistance and the total voltage is applied across the field. The speed relation of Dc shunt type motor is given as N ( V - Ia . What is an Armature? The torque developed by the motor is proportional to the armature current i.e. Permanent Magnet DC Motor. in a separately excited DC motor with armature voltage speed control, if the torque is increased and all other perimeters are left alone (i.e.
Calculate the average armature current and the motor torque. Here, we are going to calculate the power for three types of the motor based on the input supply such as DC, Single-phase and three-phase. 5.3a). The starting current is limited only by the armature resistance: / = Es/R = 150 V/l W = 150 A. b. So simplified form of the torque equation is given below: T m = T g mechanical losses i.e. i.r, Electrical power=Mechanical Power.
By multiplying the above equation by I a on both sides, we get. flux. where is in Nm, IA is in A and KV is in RPM/V.
Example 1: A 250 V dc.
Ish = V/Rsh. There exists a fundamental relationship between an electric motors velocity constant (KV), armature* current (IA) and torque (). Calculate field current \$I_f\$.
iii. Hence, $$\mathrm{\tau_{} \varpropto \varphi _{} (3)}$$ Therefore, the armature torque developed in a DC motor is directly proportional to the flux per pole and the armature current. Torque is given by the product of the force and the radius at which this force acts.
Equation (1) is the power equation of DC motor. Speed Control of Shunt DC Motors. To Calculate. DC motors, which are powered by direct current; How Electric Motors Work. r = radius of the armature in m. N = speed of the armature in rpm = N/60 rps.
400 steps/second would give 60 RPM , and 200 sps would give 30 rpm . The flux per pole is 20 mWb. Advantages of Back Emf in DC Motor. I a2 R a = Copper loss in the armature winding. The system structure of a DC motor is depicted in Figure2-2, including the armature resistance R a and winding leakage inductance L a. C. Torque required. Mathematically, torque, T = F r. Let. Constructional parameters include number of poles P, number of conductors Z and number of parallel paths a in armature. 1. (1) is multiplied by Ia on both sides, we obtain, The armature current I a includes both the field current I f and the load current I load, as I a = I f + I load. Friction and windage losses can be neglected. The SCRs are fired symmetrically at = 30 in every half cycle and the armature has a resistance of 4. e or Armature Current Motor = Angular Speed * Armature Torque / Voltage * Electrical Efficiency.Angular speed is the rate of rotation about an axis, measuring how the angle changes in a brushless DC motor).The armature
Multiplying both sides of Voltage Equation (1) by I a, we get the power equation of a DC motor as follow. Where. Equations of Voltage, Current, and Power for a Separately Excited DC Motor. E = back emf. In the DC shunt motor, the armature winding and field winding is connected in parallel. The Armature Current of Series DC Motor given Kf formula is defined as the current flows into the armature winding of the DC series motor and is represented as I a = V induced /(K f * m * s) or Armature Current Motor = Induced Voltage /(Constant based on machine construction * Magnetic Flux * Angular Speed).The Induced Voltage is described by making use of Faradays Torque produced in a DC Motor is given as. In a separately excited DC motor, field and armature windings are excited to form two various DC supply voltages. V = Eb + IaRa + BCD. The back emf opposes the supply voltage. The back emf opposes the supply voltage. In DC motor, the armature current flow in presence of air gap flux and due to an interaction of field flux and armature current, the armature conductors experiences force. The supply voltage induces the current in the coil which rotates the armature. The expression in eqn.
For example, if the total motor current was 0,203 A and the armature resistance 14,5 the power lost as heat in the windings is: Rules Of Thumb (Approximation) At 1800 rpm , a motor develops a 3 lb.ft.
The DC motor operates in linear region for servo motor application. IL = e or Armature Current Motor = Angular Speed * Armature Torque / Voltage * Electrical Efficiency.Angular speed is the rate of rotation about an axis, measuring how the angle changes Which is constant for a particular machine and therefore the torque of DC motor varies with only flux and armature current I a. The input power is the sum of the power flowing at the electrical terminals of the machine. Conversely, we may increase a DC motors speed (and reduce its torque output) by increasing the field control resistors resistance, weakening the stationary magnetic field through which the armature spins. For the DC shunt motors, the field current is constant.
Torque or moment or moment of force is the tendency of a force to rotate or move an object about an axis. The appropriate tool for studying transient response of the DC motor (or any system) is the transfer function of the system EECS461, Lecture 6, updated September 24, 2014 6. Multiplying both sides of Voltage Equation (1) by I a, we get the power equation of a DC motor as follow. "/> (1) is known as the voltage equation of the DC motor. I'm currently working on an assignment question as shown: Here's what I've tried doing: I calculated the Back E.M.F. The Armature Current of Series DC Motor given Kf formula is defined as the current flows into the armature winding of the DC series motor and is represented as I a = V induced /(K f * m * s) or Armature Current Motor = Induced Voltage /(Constant based on machine construction * Magnetic Flux * Angular Speed).The Induced Voltage is described by making use of Faradays By controlling the step rate, you control the speed. This torque acts on the mechanical structure, which is characterized by the rotor inertia J and the viscous friction coefficient F. N = Speed of rotor in RPM. Both AC and DC motors use electrical current to produce rotating magnetic fields that, in turn, generate rotational mechanical force in the armaturelocated on the rotor or statoraround the shaft. Power Equation of a DC Motor. This system is a combination of an LR circuit and mass with rotational friction. Power Equation of a DC Motor. = 2N/60 = angular speed in rads per second. It has been shown in Section 1.2 that the motor exerts a torque, while supplied by voltages on the stator and on the rotor. Apply KCL to determine \$I_a\$. The example motor you show has 400 steps per revolution. Solution : P = 4, A = P = 4, Z = 480 F = 20 mWb = 20 x 10-3 Wb, Ia = 50 A Now T a = 0.159 x ?Ia . This is expected because when current flows through the armature conductors of a DC motor, it produces flux (armature flux) which lets on the flux produced by the main poles. If it is a one percent decrement in the flux of this motor what will results? Also see: Difference Between Voltage and EMF; Ia = armature current. As the flux is directly proportional to armature current ( I a ) at a certain point the flux remains constant after its saturation point. 1.6 DESCRIBE how the speed of a DC motor is adjusted. The armature has lap connected 480 conductors. Q. In Figure 21.5 (b) the armature resistance is shown as a separate resistor in the armature circuit to help understanding. Alternatively Understanding the DC Motor Torque. System A system is any object that has one or more inputs and outputs Motor Transfer Functions , III 1 sL+R 1 J+B V V-V B K M K V I W--T L T M Transfer function from. The current flow through the armature is limited only by its resistance, and given by the Kirchhoff current law (KCL): At the very start of the motor = 0, and the induced voltage is E b = 0. In this motor, we have. Solved Problems on EMF equation of DC Generator and DC Motor Problem-1. A four-pole generator, having wave-wound armature winding has 61 slots, each slot containing 30 conductors. A. Example 1 : A 4 pole d.c. motor takes a 50 A armature current. Advantages of Back Emf in DC Motor. Circular Pitches and Equivalent Diametral Pitches Table. The current and magnetic field produce the torque and hence it is called Electromagnetic torque. = Terminal voltage - Resistance * Current (220-0.5*20 = 210), I used the formula Developed Torque * Angular velocity = E.M.F.
A 600 V, dc shunt motor has armature and field resistance of 1.5 and 600 , respectively. P= V X I. I = P/V amps, Where; V = E Ia Ra Is Rsh + brushes drop (shunt machine) V = E Ia (Ra + Rsh) + brushes drop (series machine) V = Supply Voltage. T g = armature or gross torque (N-m) = Force radius. Value of armature current is IA=(250V-245)/0.25ohm= 20 Ampere. The torque equation can be written as T e I a.I a . Where. This gave me =4.77 rad/s which gives 45.6 rpm and is really far
connected DC motors. The shunt field and armature are in parallel. Ra ) When the armature current is increased the speed value can be decreased. Therefore, for simplex wave wound dc generator, Eg = PNZ / 120 Torque equation of a DC motor When armature conductors of a DC motor carry current in the presence of stator field flux, a mechanical torque is developed between the armature and the stator. The above relation is known as Voltage Equation of the DC Motor.